Acrosome
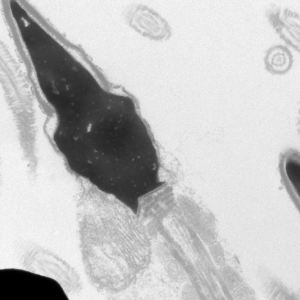
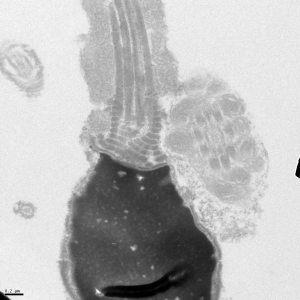
The acrosome is an organelle unique to sperm that covers the apical part of the head. Hydrolytic enzymes are contained in the acrosome, which are released during the acrosome reaction in order to break down the zona pellucida of the egg. Toxins that interfere with capacitation, such as DEHP, can result in an impaired capability to undergo the acrosome reaction.
Midpiece
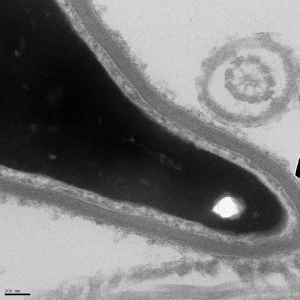
Immediately after the neck is the midpiece, which is where the mitochondria of the cell are located. One of our research interests is the potential role of mitochondrial uncouplers for sperm as a contraceptive.
Axoneme
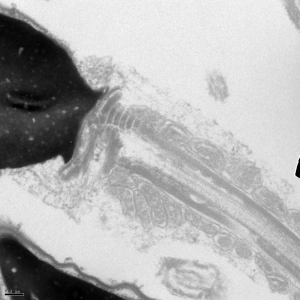
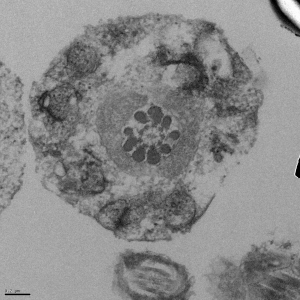
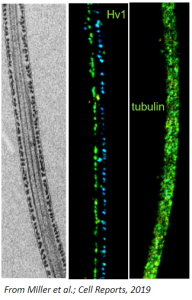
The appearance of a cross section through the flagellum differs between the principal piece and the midpiece. In the midpiece (shown above), there is a characteristic 9+2 pattern in the outer dense fibers (ODF) with a 4, 5 split. In the principal piece, two of the ODFs become the longitudinal columns, resulting in a characteristic 4, 3 split pattern. Towards the end of the tail, the ODFs are no longer present.
Principal Piece
The principal piece is the part of the flagellum that comes after the midpiece and comprises most of the flagellum. CatSper and ABHD2 in this region are responsible for hyperactivation.
Cytoplasmic droplet
The cytoplasmic droplet is not present in all sperm cells, but it allows us to perform electrophysiology when present.
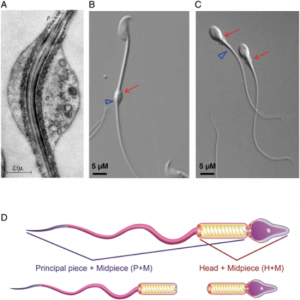
Electron micrographs for the head, acrosome, midpiece, axoneme, and neck were taken by John Della Rosa. Other images are taken from papers by Miller et al.